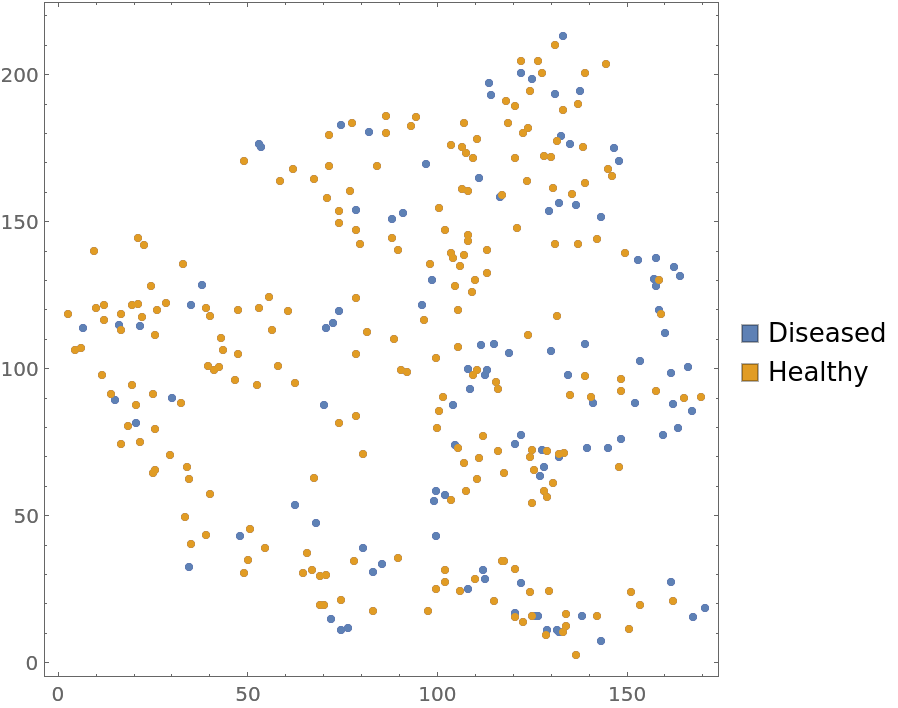
Locations of myrtles (an evergreen shrub with glossy foliage, white flowers, purple-black berries), with healthy/diseased marks
Examples
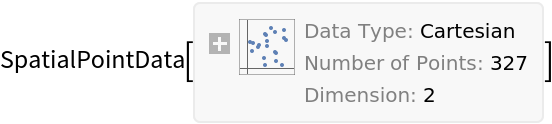
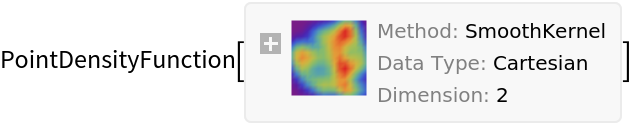
Basic Examples (1)
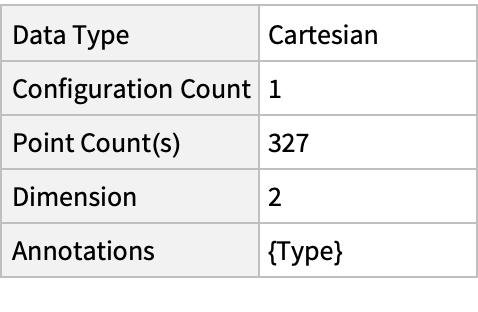
Summary of the spatial point data:
Visualizations (3)
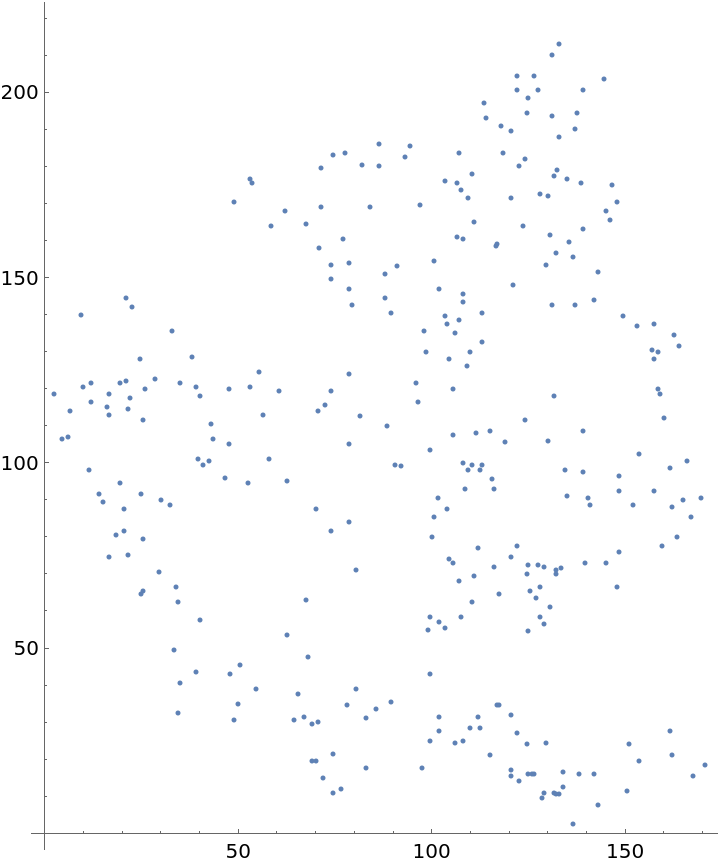
Plot the spatial point data:
Visualize the data with annotations:
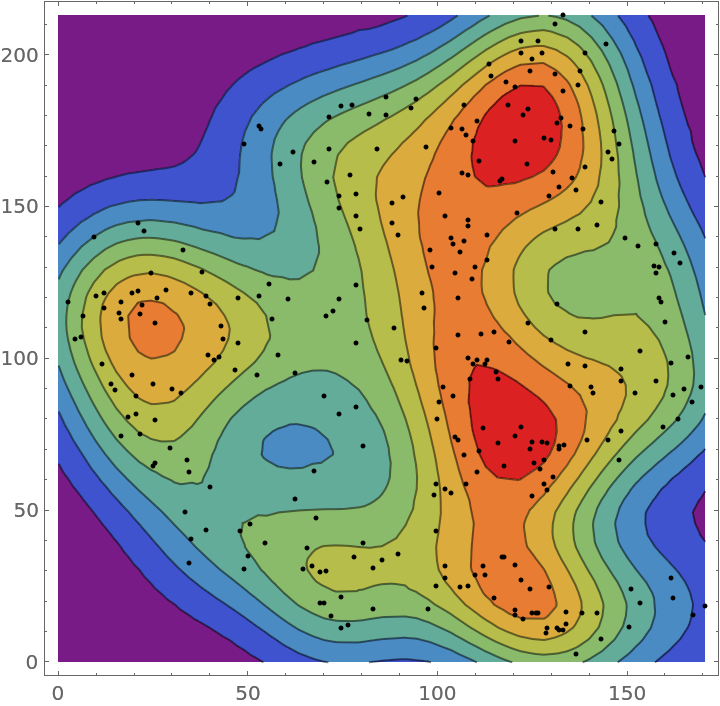
Plot the smooth point density:
Analysis (5)
Compute probability of finding a point within given radius of an existing point - NearestNeighborG is the CDF of the nearest neighbor distribution:
NearestNeighborG as the CDF of nearest neighbor distribution can be used to compute the mean distance between a typical point and its nearest neighbor - the mean of a positive support distribution can be approximated via a Riemann sum of 1- CDF. To use Riemann approximation create the partition of the support interval from 0 to maxR into 100 parts and compute the value of the NearestNeighborG at the middle of each subinterval:
Now compute the Riemann sum to find the mean distance between a typical point and its nearest neighbor:
Account for scale and units:
Test for complete spacial randomness:
Bibliographic Citation
Gosia Konwerska,
"Sample Data: Myrtles"
from the Wolfram Data Repository
(2022)
Data Resource History
Publisher Information
![Show[ContourPlot[density[{x, y}], {x, y} \[Element] ResourceData[\!\(\*
TagBox["\"\<Sample Data: Myrtles\>\"",
#& ,
BoxID -> "ResourceTag-Sample Data: Myrtles-Input",
AutoDelete->True]\), "ObservationRegion"], ColorFunction -> "Rainbow"], ListPlot[ResourceData[\!\(\*
TagBox["\"\<Sample Data: Myrtles\>\"",
#& ,
BoxID -> "ResourceTag-Sample Data: Myrtles-Input",
AutoDelete->True]\), "Data"], PlotStyle -> Black]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fe0/fe0d2cc8-136c-4d96-918c-6dd191c3b18b/2f4335af1062da4e.png)

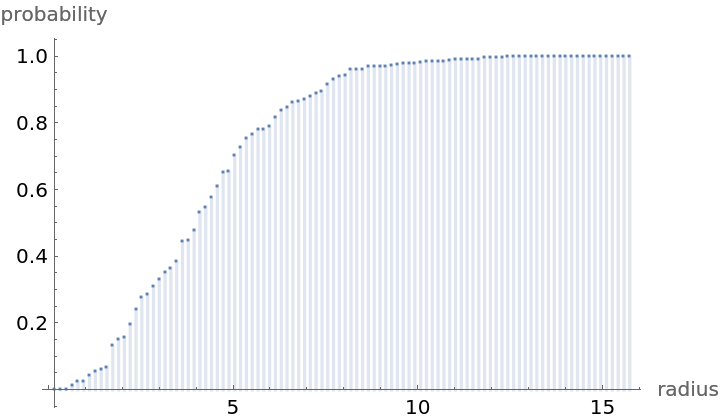
![step = maxR/100;
middles = Subdivide[step/2, maxR - step/2, 99];
values = nnG[middles];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fe0/fe0d2cc8-136c-4d96-918c-6dd191c3b18b/24d1d1c47ca1f996.png)
