Wolfram Data Repository
Immediate Computable Access to Curated Contributed Data
Observation locations of the Eurasian Collared Dove for the years 1986 to 2008 annotated with total counts
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= | 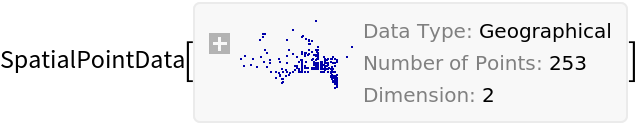 |
Summary of the spatial point data:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 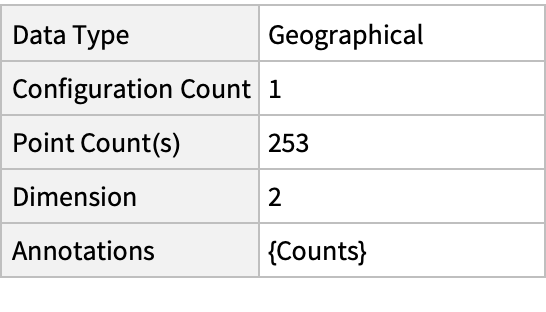 |
Plot the spatial point data:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |  |
Visualize points with annotations:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |  |
Compute probability of finding a point within given radius of an existing point - NearestNeighborG is the CDF of the nearest neighbor distribution:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |  |
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
| In[7]:= |
| Out[8]= | 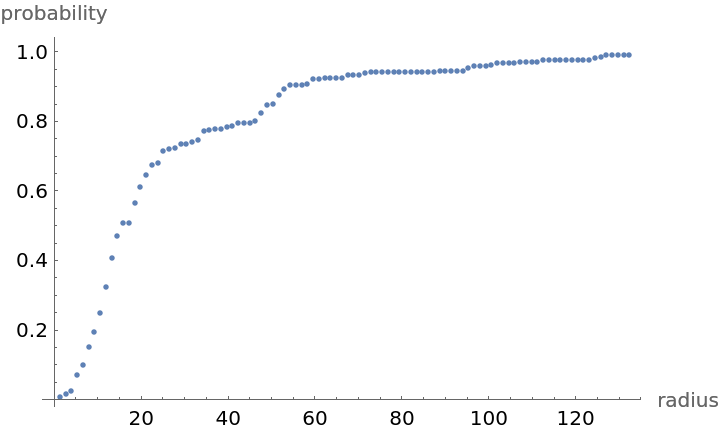 |
NearestNeighborG as the CDF of nearest neighbor distribution can be used to compute the mean distance between a typical point and its nearest neighbor - the mean of a positive support distribution can be approximated via a Riemann sum of 1- CDF. To use Riemann approximation create the partition of the support interval from 0 to maxR into 100 parts and compute the value of the NearestNeighborG at the middle of each subinterval:
| In[9]:= | ![step = maxR/100;
middles = Subdivide[step/2, maxR - step/2, 99];
values = nnG[middles];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/a97/a97af258-6538-4d95-9ee2-4beffa2ca939/01be064f845237cd.png) |
Now compute the Riemann sum to find the mean distance between a typical point and its nearest neighbor:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
Test for complete spacial randomness:
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
Gosia Konwerska, "Sample Data: Eurasian Collared Dove" from the Wolfram Data Repository (2022)